

Library
Instant access to knowledge
Our comprehensive solution
-
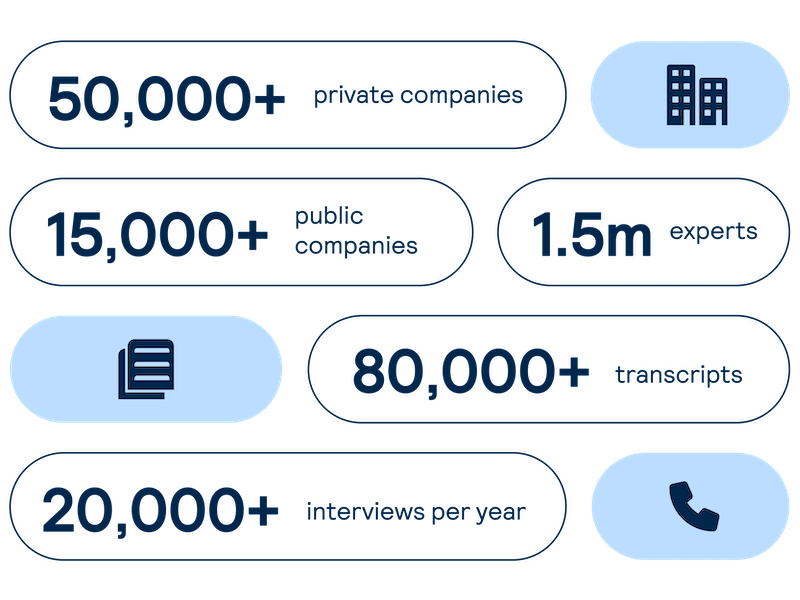
Proprietary company database
Get real-time intelligence on over 65,000 private and public companies spanning every major sector and geography, including industry value chains and market maps of competitors and customers.
-
Expert Interviews
Access comprehensive, unbiased insights on demand from interviews with industry experts led by investors and our sector analysts.
-
AI search and discoverability
Surface AI-powered insights instantly from the most comprehensive database of expert interviews, with alerts to ensure you never miss the latest insights on topics that matter to you.
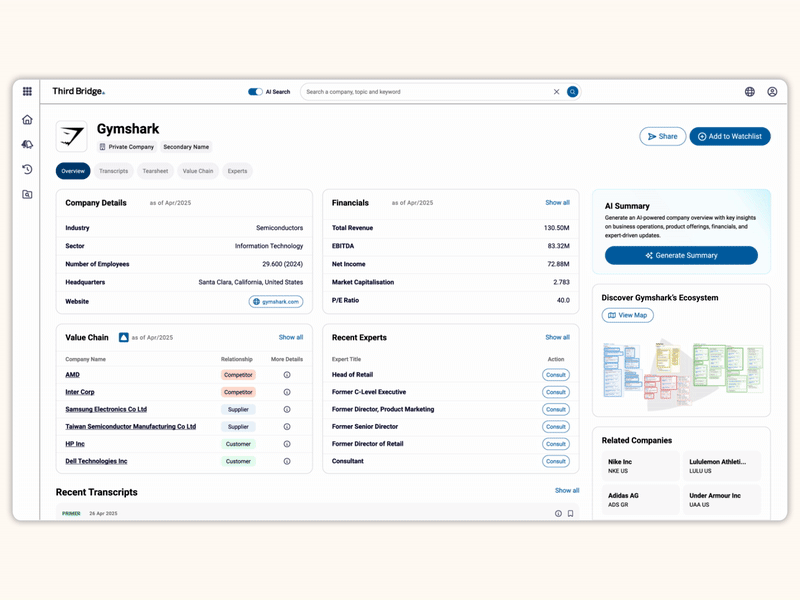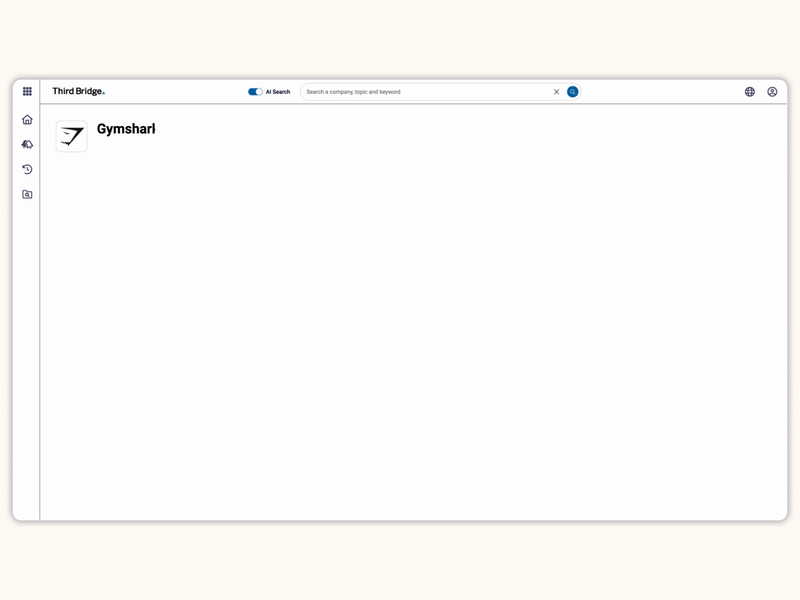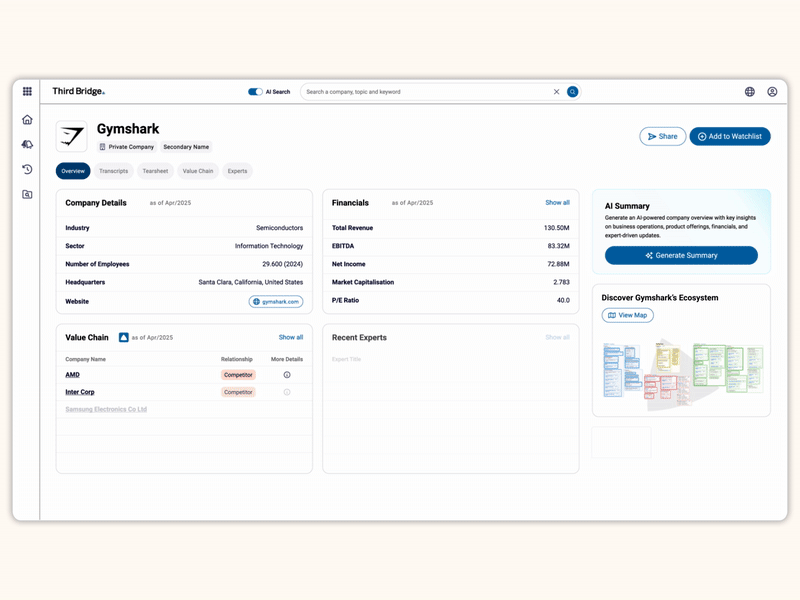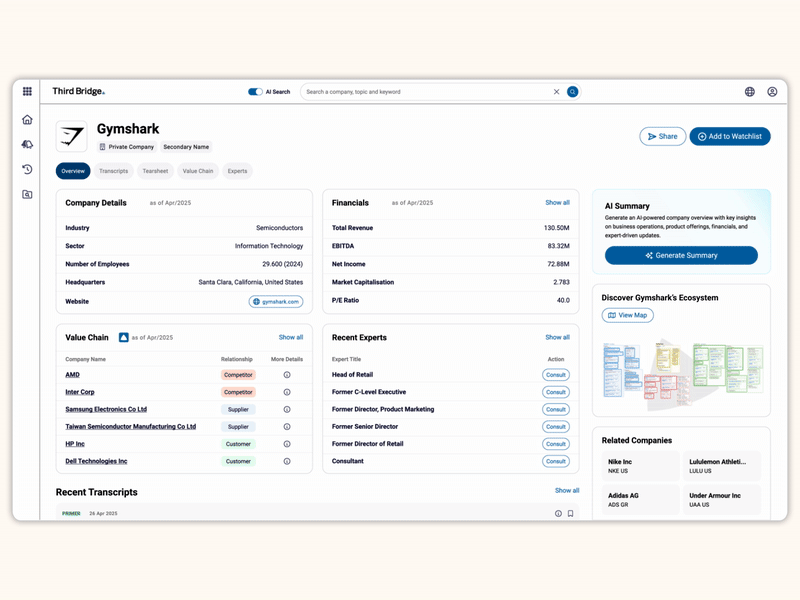
Proprietary company database
Accelerate your decision-making with instant access to detailed company profiles on over 65,000 private and public companies, compiled from high-quality expert interviews, augmented with structured data.
- Streamline early-stage research: Eliminate time-consuming preliminary diligence and quickly identify key business drivers, competitive position, growth outlook, and risks.
- 360-degree view: Gain a complete perspective on your target assets with over half a million customer, competitor, and supplier relationships, as well as value chains indexed across the database.
- Unique insights: Easily access the latest interview transcripts tailored to your investment interests to accelerate your research.
Expert interviews
Access on-demand perspectives and insights from our expert network of investors and industry specialists across public and private markets.
Our sector analysts’ deep market understanding ensures relevant insights wherever you invest, with expansive coverage across all sectors and geographies:
- Validate your thesis: Refine your assumptions with deep industry knowledge and human insights from our thoroughly screened and compliance-approved expert network.
- Filter the noise: Cut through overwhelming volumes of broker research, news, and filings to focus on the key issues identified by unbiased experts and operators.
- Build on your investment case: Follow up with any expert to deepen your understanding and explore critical issues.
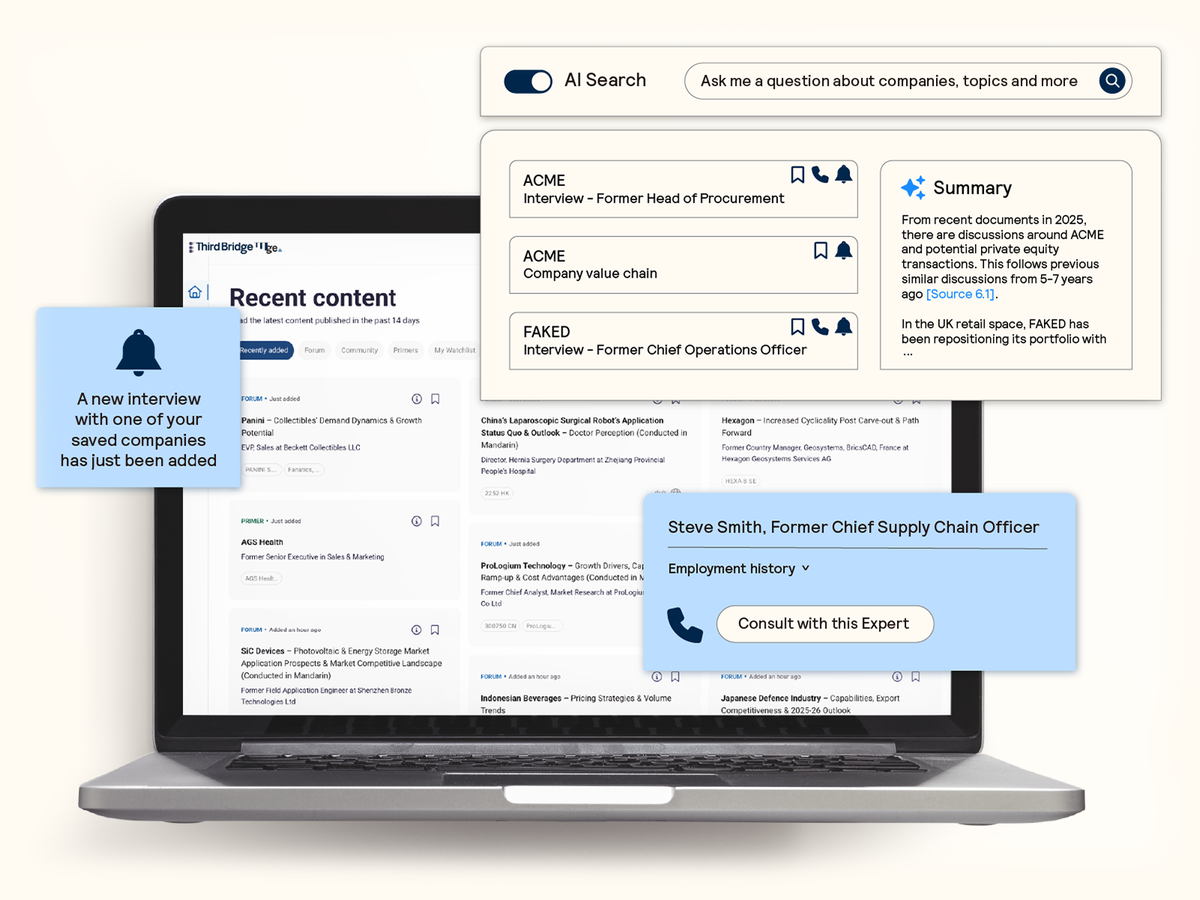
AI search and discoverability
Seamlessly identify and extract the most relevant expert insights from across the database with AI-powered search and summarization capabilities.
- Confirm your analysis: Validate your thesis with precise answers and actionable insights in response to your questions.
- Reliable intelligence: Attribute insights to transparent and robust citations that link directly back to real experts.
- Regular updates: Receive alerts on topics and companies of interest to ensure you never miss the latest insights.
Third Bridge helps us ask better questions during diligence because we're more informed. Without fail this leads to a better outcome for us and our LPs.
We look at companies dealing with enhanced risk exposure, so extracting nuanced information directly from those in the know is critical to success. Third Bridge is an absolute must-have for us.
What we like about Third Bridge is that it often takes our attention away from consensus opinion pushed by other research providers, and that’s where we typically get ahead of the market.
Explore our other services
-
Data feeds
Third Bridge content, seamlessly integrated into your research and analytics workflows.
-
Expert calls
A direct conversation with experts who have the right industry knowledge, whatever your focus.
-
Advisors
Long-term advisory support at a fraction of the cost of traditional headhunters.
-
Surveys
Quantitative and qualitative insights at scale from the highest quality respondents within 72 hours.
